EchoLink Mini
DIY ESP32 Walkie-Talkie with I2S Audio and ESP-NOW — "EchoLink Mini"
If you've ever dreamed of building a digital walkie-talkie from scratch, one that works without the internet, routers, or cellular networks, you're in the right place. Introducing EchoLink Mini, a compact, low-latency wireless voice communicator powered by ESP32, I2S audio components, and ESP-NOW.
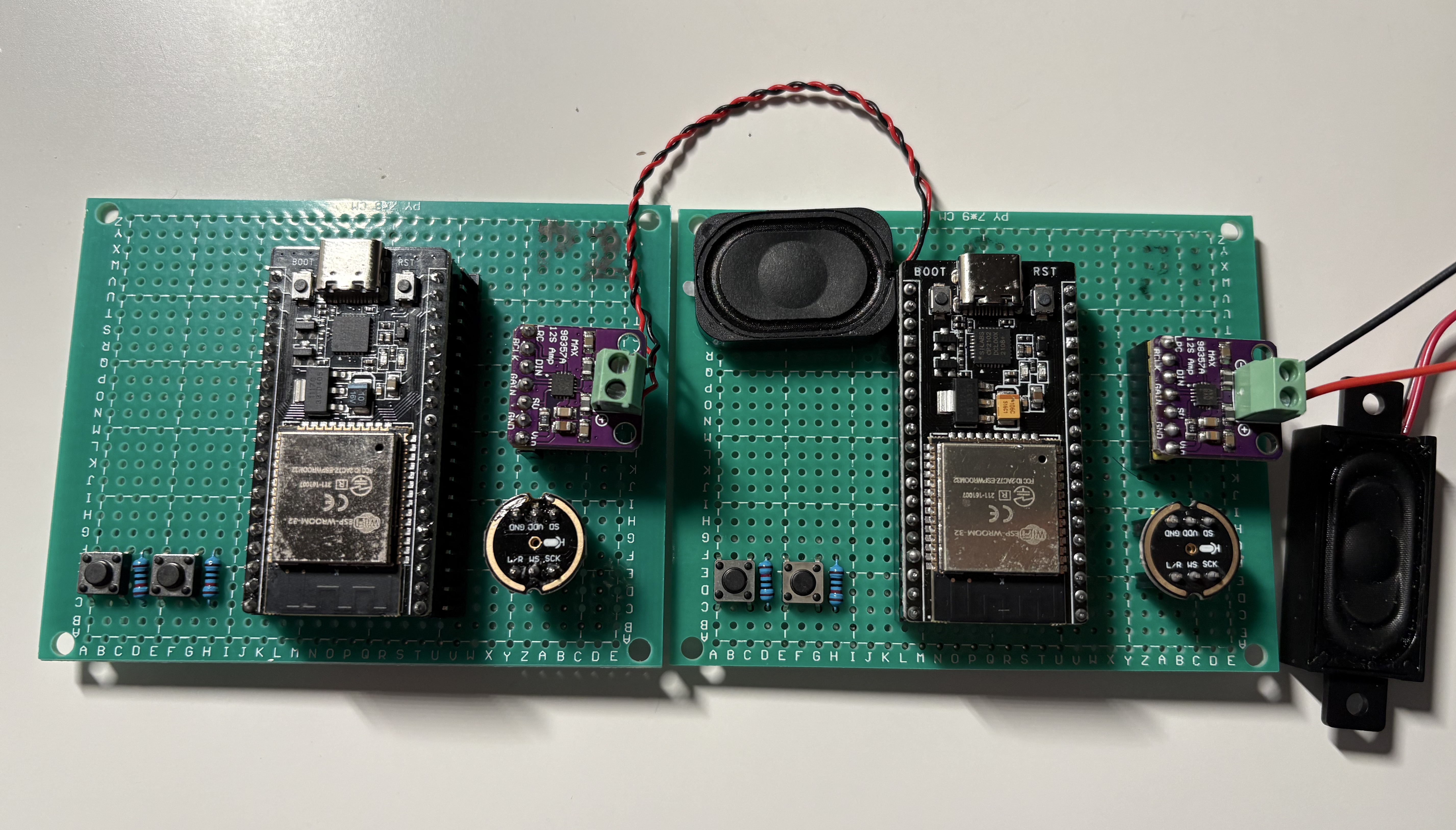
🎯 What Is EchoLink Mini?
EchoLink Mini is a fully DIY digital walkie-talkie built using two ESP32 boards. It uses MEMS digital microphones (INMP441), I2S audio playback modules (MAX98357), and ESP-NOW for wireless communication — no Wi-Fi or Bluetooth pairing required.
It supports:
- Real-time half-duplex voice transmission
- Push-to-talk (PTT) operation
- µ-Law audio compression
- Low latency (~150ms end-to-end)
- Compact design, battery operated
🧩 Hardware List
Each EchoLink Mini unit contains:
- ESP32 DevKit board
- INMP441 I2S microphone
- MAX98357 I2S DAC amplifier
- 3W 4Ω speaker
- Push-to-talk button (GPIO)
- 18650 battery + TP4056 charger + boost converter (5V)
- Optional: OLED screen, SD card, volume knob
🛠️ Core Technologies
1. I2S Audio Chain
- Recording: INMP441 captures 16-bit mono PCM audio at 16kHz via I2S0
- Playback: MAX98357 outputs decoded audio via I2S1
- Compression: µ-Law encoding (G.711) to reduce bandwidth to 8kHz, 8-bit
2. ESP-NOW Wireless
ESP-NOW is a fast, connectionless protocol built on Wi-Fi that allows peer-to-peer communication without a router. It’s perfect for short audio packets (e.g. 200 bytes every 25ms).
3. FreeRTOS Tasks
micTask(): samples audio, compresses, sendsspeakerTask(): receives, decompresses, plays- Circular buffers and task queues keep the latency low and jitter minimal
🔋 Power Supply
EchoLink Mini is designed to run portably using a single 18650 Li-ion battery. The TP4056 manages charging and protection, while a boost converter supplies stable 5V to the ESP32 and audio modules.
🧠 Why µ-Law?
Using µ-Law encoding reduces audio data to 1/4th its size with minimal perceptual loss. It enables the system to run full-duplex audio within the ESP-NOW data limit (250 bytes max).
🗨️ Use Cases
- Team intercom in workshops or maker labs
- Classroom or training room assistant
- Walkie-talkie for hiking trips (no cellular coverage)
- Experimental voice IoT
🌱 Possible Extensions
- Add OLED for UI (channel, battery)
- Volume control via potentiometer
- VOX (voice-activated transmit)
- Multi-channel pairing or ID broadcast
- Encryption (ESP-NOW supports PMK)
- Replace µ-Law with Opus for better quality
📦 Source Code
The full open-source Arduino code is available on GitHub with PlatformIO support.
🎉 Final Thoughts
EchoLink Mini is not just a walkie-talkie — it's a proof of concept for low-power, real-time audio communication using ESP32s without relying on traditional wireless infrastructure.
Whether you're building it for fun, education, or as a foundation for something bigger, it's a rewarding and surprisingly high-performance project.
Let your voice be heard — wirelessly, efficiently, and entirely offline.
🛠️ Built with love, one packet at a time.
/*
* ESP32 Walkie‑Talkie (Half‑Duplex)
* -------------------------------------------------------------
* Hardware
* – ESP32‑DevKit (two identical nodes)
* – INMP441 I2S MEMS microphone
* – MAX98357A I2S DAC/amp + 3 W speaker
* – Push‑to‑talk switch on GPIO0 (active LOW)
* – Optional micro‑SD (for debug recordings)
*
* Network layer
* ESP‑NOW (fast, connection‑less, ≤ 250 B payload)
* Both nodes run identical firmware. At first start each node
* prints its Wi‑Fi MAC in the serial console (115200 baud). Put
* the peer’s MAC into PEER_MAC below and re‑flash.
*
* Audio layer
* – 16 kHz, 16‑bit, mono PCM from mic (I2S0 in RX‑only mode)
* – µ‑Law companding to 8 kHz, 8‑bit (4× compression)
* – Packet = 200 bytes payload → 25 ms of audio → 40 packets s‑1
* – Jitter buffer 4 packets (≈ 100 ms) on receive side
*
* Build
* PlatformIO / VS Code, env = esp32dev, Arduino framework.
* Serial monitor @ 115200.
* -------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <driver/i2s.h>
#include <esp_wifi.h>
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- PIN ASSIGNMENTS ------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
// SD Card (optional)
#define SD_CS 5
#define SPI_MOSI 23
#define SPI_MISO 19
#define SPI_SCK 18
// Speaker I2S (MAX98357)
#define I2S_DOUT 27 // DATA out to DAC
#define I2S_BCLK 26 // Bit‑clock
#define I2S_LRC 25 // Word‑select / LRCLK
// Mic I2S (INMP441) – fixed pins, do not swap
#define MIC_WS 14 // Word‑select
#define MIC_SD 33 // Data OUT from mic → ESP32 IN
#define MIC_SCK 32 // Bit‑clock
#define PTT_PIN 23 // Push‑to‑talk (active LOW)
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- AUDIO PARAMETERS -----------------
//--------------------------------------------------
static constexpr uint32_t SAMPLE_RATE_HZ = 16000; // PCM input
static constexpr size_t PCM_SAMPLES_PKT = 400; // 25 ms @ 16 kHz
static constexpr size_t MULAW_PKT = 200; // µ‑Law 8 kHz
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- ESP‑NOW CONFIG -------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
// Put the peer’s base‑10 MAC bytes here before flashing.
// P1 MAC = A0:A3:B3:2C:B9:94
// P2 MAC: CC:DB:A7:2F:48:D8
uint8_t PEER_MAC[6] = {0xA0, 0xA3, 0xB3, 0x2C, 0xB9, 0x94}; // P1 MAC
// uint8_t PEER_MAC[6] = {0xCC, 0xDB, 0xA7, 0x2F, 0x48, 0xD8}; //P2 MAC
// A queue feeding speaker (PCM16)
static QueueHandle_t spkQueue;
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- µ‑Law CODEC ------------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
// Basic ITU‑T G.711 µ‑Law implementations (lookup tables).
static inline uint8_t linearToMuLaw(int16_t pcm)
{
const uint16_t MULAW_MAX = 0x1FFF; // 8191
const uint8_t MULAW_BIAS = 33;
uint16_t mask;
uint16_t seg;
uint8_t uval;
pcm = pcm >> 2; // 14‑bit dynamic range
mask = (pcm < 0) ? 0x7F : 0xFF;
if (pcm < 0) pcm = -pcm;
if (pcm > MULAW_MAX) pcm = MULAW_MAX;
pcm += MULAW_BIAS;
/* Convert the scaled magnitude to segment number. */
seg = 0;
uint16_t temp = pcm;
for (seg = 0; seg < 8; seg++) {
if (temp <= 0x1F) break;
temp >>= 1;
}
/* Combine the sign, segment, and quantization bits. */
uval = (~((seg << 4) | ((pcm >> (seg + 1)) & 0xF))) & mask;
return uval;
}
static inline int16_t muLawToLinear(uint8_t u_val)
{
const int16_t exp_lut[8] = {0, 132, 396, 924, 1980, 4092, 8316, 16764};
u_val = ~u_val;
int16_t t = ((u_val & 0xF) << 3) + 132;
t <<= ((unsigned)u_val & 0x70) >> 4;
return (u_val & 0x80) ? (132 - t) : (t - 132);
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- I2S INITIALISATION -----------------
//--------------------------------------------------
static void initMic()
{
i2s_config_t micCfg = {
.mode = (i2s_mode_t)(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX),
.sample_rate = SAMPLE_RATE_HZ,
.bits_per_sample = I2S_BITS_PER_SAMPLE_16BIT,
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT,
.communication_format = I2S_COMM_FORMAT_STAND_I2S,
.intr_alloc_flags = ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1,
.dma_buf_count = 4,
.dma_buf_len = PCM_SAMPLES_PKT,
.use_apll = false,
.tx_desc_auto_clear = false,
.fixed_mclk = 0
};
i2s_pin_config_t micPins = {
.bck_io_num = MIC_SCK,
.ws_io_num = MIC_WS,
.data_out_num = -1,
.data_in_num = MIC_SD
};
i2s_driver_install(I2S_NUM_0, &micCfg, 0, nullptr);
i2s_set_pin (I2S_NUM_0, &micPins);
}
static void initSpeaker()
{
i2s_config_t spkCfg = {
.mode = (i2s_mode_t)(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_TX),
.sample_rate = SAMPLE_RATE_HZ,
.bits_per_sample = I2S_BITS_PER_SAMPLE_16BIT,
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT,
.communication_format = I2S_COMM_FORMAT_I2S_MSB,
.intr_alloc_flags = ESP_INTR_FLAG_LEVEL1,
.dma_buf_count = 4,
.dma_buf_len = PCM_SAMPLES_PKT,
.use_apll = false,
.tx_desc_auto_clear = true,
.fixed_mclk = 0
};
i2s_pin_config_t spkPins = {
.bck_io_num = I2S_BCLK,
.ws_io_num = I2S_LRC,
.data_out_num = I2S_DOUT,
.data_in_num = -1
};
i2s_driver_install(I2S_NUM_1, &spkCfg, 0, nullptr);
i2s_set_pin (I2S_NUM_1, &spkPins);
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- ESP‑NOW CALLBACKS ------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
static void onDataRecv(const uint8_t *mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len)
{
// Each byte is µ‑Law, 25 ms frame.
static int16_t pcmBuf[PCM_SAMPLES_PKT];
if (len != MULAW_PKT) return; // sanity check
for (int i = 0; i < MULAW_PKT; ++i)
pcmBuf[i] = muLawToLinear(incomingData[i]);
// Push to speaker queue (ISR‑safe version)
if (xQueueSendFromISR(spkQueue, pcmBuf, nullptr) != pdTRUE) {
// queue full → drop
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- TASKS ------------------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
void micTask(void *pv)
{
static int16_t pcm[PCM_SAMPLES_PKT];
static uint8_t ulaw[MULAW_PKT];
size_t bytesRead;
while (true) {
// Wait until PTT pressed (LOW)
if (digitalRead(PTT_PIN) == LOW) {
i2s_read(I2S_NUM_0, pcm, sizeof(pcm), &bytesRead, portMAX_DELAY);
if (bytesRead != sizeof(pcm)) continue;
// Downsample 16 kHz→8 kHz: drop every other sample
for (size_t i = 0, j = 0; i < PCM_SAMPLES_PKT; i += 2, ++j) {
int16_t s = pcm[i];
ulaw[j] = linearToMuLaw(s);
}
esp_now_send(PEER_MAC, ulaw, sizeof(ulaw));
} else {
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(10));
}
}
}
void speakerTask(void *pv)
{
static int16_t pcm[PCM_SAMPLES_PKT];
size_t bytesWritten;
while (true) {
if (xQueueReceive(spkQueue, pcm, portMAX_DELAY) == pdTRUE) {
// Duplicate samples to restore 8→16 kHz (naïve interp.)
static int16_t up[PCM_SAMPLES_PKT];
for (int i = 0; i < MULAW_PKT; ++i) {
up[i * 2] = pcm[i * 1];
up[i * 2 + 1] = pcm[i * 1];
}
i2s_write(I2S_NUM_1, up, sizeof(up), &bytesWritten, portMAX_DELAY);
}
}
}
//--------------------------------------------------
// ---------- SETUP ------------------------------
//--------------------------------------------------
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
pinMode(PTT_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
// Print MAC so user can copy to peer
Serial.print("My MAC: "); Serial.println(WiFi.macAddress());
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
esp_wifi_set_ps(WIFI_PS_NONE); // disable power‑save for latency
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("ESP‑NOW init failed");
ESP.restart();
}
esp_now_register_recv_cb(onDataRecv);
esp_now_peer_info_t peer{};
memcpy(peer.peer_addr, PEER_MAC, 6);
peer.channel = 0; // same channel
peer.encrypt = false;
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peer) != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
}
initMic();
initSpeaker();
spkQueue = xQueueCreate(8, sizeof(int16_t) * PCM_SAMPLES_PKT);
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(micTask, "mic", 4096, nullptr, 1, nullptr, 0);
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(speakerTask, "speaker", 4096, nullptr, 1, nullptr, 1);
Serial.println("Walkie‑talkie ready. Hold PTT (GPIO0) to talk.");
}
void loop()
{
vTaskDelay(pdMS_TO_TICKS(1000));
}
